How Do You Determine Which Adiabatic Rate to Use
All Ts and Ps are absolute value. In this question initial altitude or height 0 km final altitude 12 km initial temperature 12 degrees C and final temperature -54 degrees C.
Chapter 5 Atmospheric Stability Atmospheric Processes And Phenomenon
For this to be the case the process must be fast so that no heat is exchanged with the environment.
. Where ΔcH T1 is the standard molar enthalpy of combustion at the initial temperature. The value of the adiabatic flame temperature given in Equation 155 is for 100 completion of the reaction. The sum of ΔH rxnT1and ΔH P is zero and we can write.
In this regard how do you calculate lapse rate. T - duration of fault current s. For example for the combustion of hydrogen and oxygen at high temperatures the combustion product water dissociates back.
Assumes a dry parcel of airAir cools 3C100 m rise in altitude 54F1000 ft. By inspection the lapse rate for layer B-C has a slope that is parallel to the nearest dry adiabatic lapse rate. I - the fault current in A.
The environmental lapse rate is calculated in terms of a stationary atmosphere and may also be referred to as the temperature gradient. Meaning the term implies that no heat is loss or gained. Here we demonstrate an adiabatic equation example we will explain how the adiabatic equation calculator works.
The adiabatic process is fundamental to the analysis of water rockets. Moist or saturated adiabatic lapse rate and the dry adiabatic lapse rate are the two types of lapse rates. 2The term adiabatic refers to the unchanging external heat.
Using time current graph number 1. The adiabatic-temperature rise can be calculated for any reaction of interest and thus it is often useful in the analysis and design. Knowing compressor polytropic efficiency provided by the vendor calculate n by equation 6 the 2nd one on the right hand side.
For a given fault of I which lasts for time t the minimum required cable cross-sectional area is given by. So in the first law of thermodynamics we can anticipate that we will set the dQ term equal. Enter a measured voltage value Uo 230V.
A typical value is around 5 Ckm 27 F1000 ft 15 C1000 ft. Use equation 7 to estimate the adiabatic efficiency the Greek letter mu. Therefore the A-B layer is STABLE.
Adiabatic compression is a process where there the PV work done is negative and it results in increase temperature of system. In this calculator you have three input values. Change of temperature with a change in altitude of an air parcel without gaining or losing any heat to the environment surrounding the parcel.
This rise in temperature increases the internal energy of the system. Initial altitude or elevation. Adiabatic compression assumes perfect insulation which is purely theoretical.
The first order explanation is the dry adiabatic lapse rate. When the air is saturated with water vapour at its dew point the moist adiabatic lapse rate MALR or saturated adiabatic lapse rate SALR applies. Wet adiabatic lapse rate.
In general a lapse rate measures rate at which temperature changes with changes in altitude. A I 2 t k. The reason for the difference between the dry and moist adiabatic.
This calculator calculates the final temperature of an air parcel that rises adiabatically as long as air is not saturated. 12 2 x -55 12 - 11 C. An adiabatic process means no heat is exchanged in the process.
In reality as the temperature increases the tendency is for the degree of reaction to be less than 100. As parcel rises H 2 O condenses and gives off heat and warms air around it. The heat of the parcel of air is stable and does not change with the.
Adiabatic assumption can however be safely made by engineers for all. The adiabatic process can be either reversible or irreversible. The dry adiabatic lapse rate is 98 Kkm.
One use is with combustion reactions whereby it is useful for determining the adiabatic-flame temperature. T 01s 1966A This is perfectly acceptable maximum disconnection time 5 seconds over 32A I will now use the adiabatic equation below to confirm that the armouring of the cable can withstand the level of fault current. Thus the lapse rate is -55 Ckm that is with each km rise in altitude the temperature will fall by 55 degrees C.
A - the nominal cross-section area mm 2. The thermodynamic process in which there is no exchange of heat from the system to its surrounding neither during expansion nor during compression. ΔξΔcH T1 T2T1Cp PdT 0.
An adiabatic process is defined as. Dry adiabatic lapse rate. The reaction is notoriously endothermic so I am not sure I would use the term adiabatic with required down stream water gas shift reactions to produce H2.
The environmental lapse rate is found by dividing the change in temperature by the change in altitude. Predicting an adiabatic-temperature rise is useful to chemical engineers for a number of purposes. 1Lapse rates imply warming and cooling of air.
Select to solve for a different unknown. P1 and P2 are the suction and discharge pressures respectively. Uo is the voltage to earth.
Water Rockets - the transportation system of the future tounge-in-cheek Engineering Thermodynamics by Israel Urieli is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 30 United States License. Rate of decrease is. The normally used equation is the so-called adiabatic equation.
This lapse rate varies strongly with temperature. The voltage value needs to be a measured value in-order to carry out an accurate calculation. Following are the essential conditions for the adiabatic process to take place.
You can see this simply by inspection the A-B part of the sounding leans more to the right than either of the nearby adiabatic bench mark lines.

Adiabatic Lapse Rate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

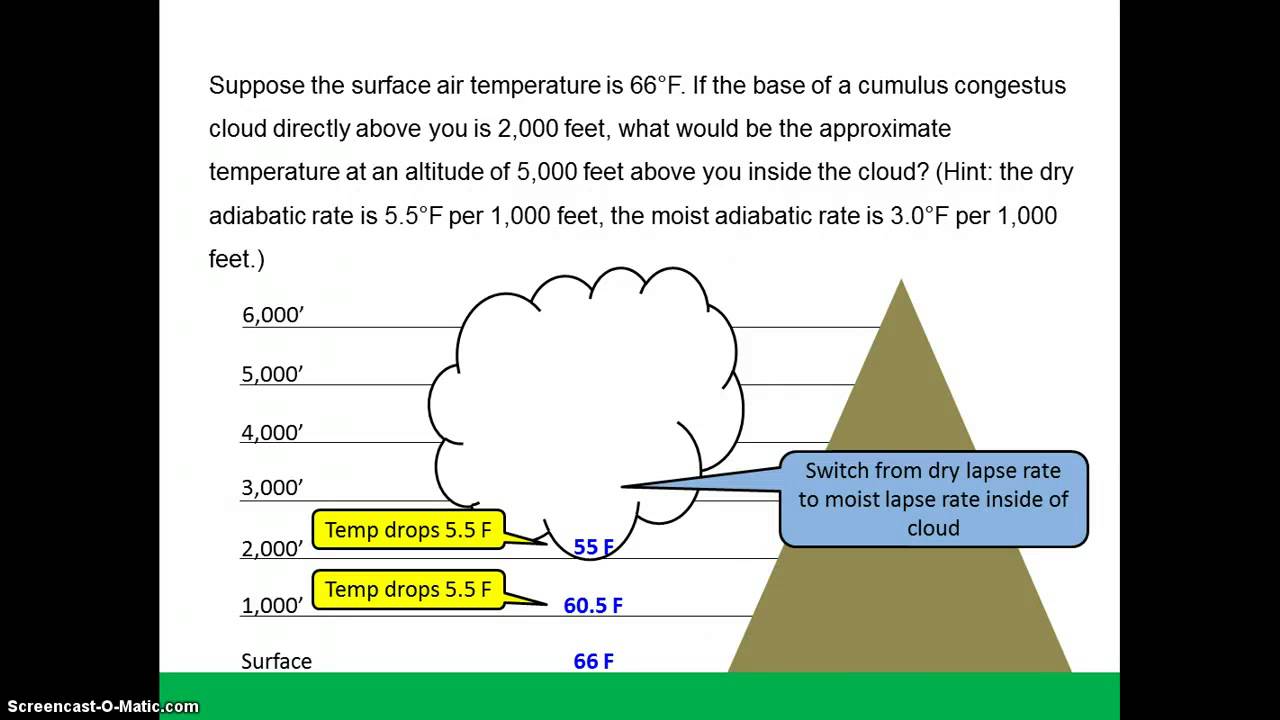
Atmospheric Stability Ppt Download

Calculating Adiabatic Changes In Temperature And Humidity Youtube
No comments for "How Do You Determine Which Adiabatic Rate to Use"
Post a Comment